
配置篇-suricata.yaml-2
本文接上一篇配置文件说明1,是了解suricata配置文件的第二篇。suricata版本为4.0.3。
threading
Suricata是一个多线程的程序,当它在拥有多核CPU的计算机上运行时会产生多线程以同时处理多个网络流量。在前一篇文章中介绍过suricata其实是有thread,thread-module和queue组成,而thread-module按照功能分为数据包获取、解码数据包和应用层流信息、检测、输出四种模块。
- 数据包获取模块是从网络流量或文件中获取数据包。
- 解码前面获取的数据包,如果是基于TCP协议的流则需要分三步:首先是跟踪每一条流的所有链接信息,然后使用流重组(stream-assembly)对已经完成的流进行重组,最后则是根据对应的应用层协议对其进一步分析,比如HTTP协议有专门的分析模块。
- 检测模块则是对上一步解码或重组的流量进行检测。检测模块可以是多线程因此它可以同时检测多个数据包或流。
- 输出模块则会针对配置文件中的配置,对所有的警告、事件以及需要输出的额外信息进行处理并格式化输出。
下面这个图是一种典型的运行模式表明了模块间的协作关系,1、2、3、4分别代表四种模块:
Suricata的多个线程通过下面的选项可以选择是否绑定特定的CPU核心,如果是no则不绑定,每次运行的时候每个线程对应的CPU核心可能都不是同一个,是yes则每次运行的时候指定的线程只能运行在特定的核心上。通过绑定线程和CPU核心,能够提高CPU cache的命中率,减少内存访问的损耗,提高程序的运行速度:
set-cpu-affinity: no下面这幅图可以很清楚地解释。上面的是绑定的情况,数据包获取、解密和输出模块均在core 0这个核心上,且每个核心都有一个detect线程,但是相对来说其在core 0上的优先级比较低,只有当core 0的其他线程不工作时才会运行,这样suricata也会把较少的检测任务分配给它,而是分配给其他核心上的检测线程;但是如果是下面哪种未绑定的情况,则是由系统根据CPU每个核心的负载程度来分配每个线程运行所在的核心:
用户可以根据自己的具体情况配置线程和CPU核心的对应关系,下面是一种配置方法,management-, receive-, decode-, stream-, detect-, verdict-, reject-和outputs-set这些字段都是固定的,每个字段拥有cpu、mode和prio三个选项。cpu自然就是选择线程执行的cpu核心编号,数字从0到3或是all,[0,1]表示core 0和core 1,[1-3]表示core 1,core 2, core 3三个核心。mode可以“balance”或“exclusive”,balance表示可以在所有cpu字段定义的核心中选择最合理的核心运行,比如下面的decode-cpu-set这次可以在core 0上种运行,等下个时间片可以在core 1上运行;而exclusive则表示固定cpu核心,第一次时间片在core 0上运行,直到线程结束都不能更换核心。prio则是线程在核心中的权限高低,有low,medium和high以及default。除此之外在detect-cpu-set中还可以有threads字段直接指定检测线程的数量而不是根据CPU核心数来计算:
# Tune cpu affinity of threads. Each family of threads can be bound
# on specific CPUs.
#
# These 2 apply to the all runmodes:
# management-cpu-set is used for flow timeout handling, counters
# worker-cpu-set is used for 'worker' threads
#
# Additionally, for autofp these apply:
# receive-cpu-set is used for capture threads
# verdict-cpu-set is used for IPS verdict threads
#
cpu-affinity:
- management-cpu-set:
cpu: [ 0 ] # include only these cpus in affinity settings
- receive-cpu-set:
cpu: [ 0 ] # include only these cpus in affinity settings
- worker-cpu-set:
cpu: [ "all" ]
mode: "exclusive" # run detect threads in these cpus
# Use explicitely 3 threads and don't compute number by using
# detect-thread-ratio variable:
# threads: 3
prio:
low: [ 0 ]
medium: [ "1-2" ]
high: [ 3 ]
default: "medium"
#- verdict-cpu-set:
# cpu: [ 0 ]
# prio:
# default: "high"上面提到的检测线程的数量可以直接指定,也可以根据CPU核心数计算,而计算的系数就是由detect-thread-ratio来指定,默认系数是1.0,比如你的CPU是4核,detect-thread-ratio系数是1.5,那就会有6个检测线程:
detect-thread-ratio: 1.0IP Defrag
在之前介绍suricata规则检测IP头的时候介绍过,IP协议可以对较大的数据进行分片传输,然后在目的端进行重组,suricata中就有一个叫做defragment-engine的模块对分片的IP数据包进行监视和重组然后传给后续的处理模块。配置比较简单,max-frags指出最大的分片数量,prealloc表明是否在程序启动时预分配部分空间,timeout则是超时的时间。因为在数据包监测及重组的过程中,未处理的数据包都会在内存中,如果数量太大或是长时间未进行处理就会降低性能:
# Defrag settings:
defrag:
memcap: 32mb
hash-size: 65536
trackers: 65535 # number of defragmented flows to follow
max-frags: 65535 # number of fragments to keep (higher than trackers)
prealloc: yes
timeout: 60Flow和Stream
在suricata中flow配置的是网络流方面的选项,而stream则专门针对TCP协议的重组进行配置。
flow
flow在概念上比较大,它和一次网络连接比较相似。Suricata通过五元组(协议,源IP,源端口,目的IP,目的端口)来识别流量中的数据包是否属于同一个流:
持续的跟踪网络中的流需要占用大量的内存,为了控制占用的内存不至于太大,这里有几个选项需要配置。memcap表示最大跟踪流量所使用的内存,默认为128MB;由于suricata是通过五元组计算出一个hash值判断数据包属于哪个流,hash_size指的就是这个hash表的大小;Prealloc表示预先分配的内存,这样在识别流的时候会有更好的性能;emergency-recovery表示的是当前占用的内存大于memcap时进入内存紧急模式(emergency-mode),需要删除的流的百分比(相对于prealloc来说),这里表示需要删除30%的prealloc设置的空间的流,而删除的原则是根据后面会配置的flow-timeouts也就是超时时间来确定,如果没有流超时则会设置更严格的超时时间,如果还是没用suricata会删除最久未使用过的流;prune_flows表示处于紧急模式的时候每新增一条流将会删除掉旧的流的数量:
# Flow settings:
# By default, the reserved memory (memcap) for flows is 32MB. This is the limit
# for flow allocation inside the engine. You can change this value to allow
# more memory usage for flows.
# The hash-size determine the size of the hash used to identify flows inside
# the engine, and by default the value is 65536.
# At the startup, the engine can preallocate a number of flows, to get a better
# performance. The number of flows preallocated is 10000 by default.
# emergency-recovery is the percentage of flows that the engine need to
# prune before unsetting the emergency state. The emergency state is activated
# when the memcap limit is reached, allowing to create new flows, but
# prunning them with the emergency timeouts (they are defined below).
# If the memcap is reached, the engine will try to prune flows
# with the default timeouts. If it doens't find a flow to prune, it will set
# the emergency bit and it will try again with more agressive timeouts.
# If that doesn't work, then it will try to kill the last time seen flows
# not in use.
# The memcap can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates it's
# in bytes.
flow:
memcap: 128mb # The maximum amount of bytes the flow-engine will make use of.
hash-size: 65536 # Flows will be organized in a hash-table. With this option you can set the.
# size of the hash-table.
prealloc: 10000 # The amount of flows Suricata has to keep ready in memory.
emergency-recovery: 30 # Percentage of 1000 prealloc'd flows.
#managers: 1 # default to one flow manager
#recyclers: 1 # default to one flow recycler threadflow-timeouts
上一节中提到的流的超时时间在此处设置。由于协议的不同,因此需要对不同的协议设置不同的阶段,对应的超时时间也会不同。TCP协议包括新建连接,建立连接和关闭连接,UDP只有新建连接和建立连接两个阶段。
TCP新建连接就是三次握手,建立连接则是完成三次握手之后,而关闭连接则是reset数据包或是关闭tcp连接的四次握手。UDP新建连接是只有一方发送数据包,建立连接则是两方都发送数据包。下面是TCP、UDP、ICMP和default(其他协议)的超时配置,没有emergency前缀的是正常模式下的超时,带有emergency前缀的是在内存紧急模式下的超时时间:
# Specific timeouts for flows. Here you can specify the timeouts that the
# active flows will wait to transit from the current state to another, on each
# protocol. The value of "new" determine the seconds to wait after a hanshake or
# stream startup before the engine free the data of that flow it doesn't
# change the state to established (usually if we don't receive more packets
# of that flow). The value of "established" is the amount of
# seconds that the engine will wait to free the flow if it spend that amount
# without receiving new packets or closing the connection. "closed" is the
# amount of time to wait after a flow is closed (usually zero). "bypassed"
# timeout controls locally bypassed flows. For these flows we don't do any other
# tracking. If no packets have been seen after this timeout, the flow is discarded.
#
# There's an emergency mode that will become active under attack circumstances,
# making the engine to check flow status faster. This configuration variables
# use the prefix "emergency-" and work similar as the normal ones.
# Some timeouts doesn't apply to all the protocols, like "closed", for udp and
# icmp.
flow-timeouts:
default:
new: 30 # Time-out in seconds after the last activity in this flow in a New state.
established: 300 # Time-out in seconds after the last activity in this flow in a Established state.
closed: 0
bypassed: 100
emergency-new: 10 # Time-out in seconds after the last activity in this flow in a New state during the emergency mode.
emergency-established: 100 # Time-out in seconds after the last activity in this flow in a Established state in the emergency mode.
emergency-closed: 0
emergency-bypassed: 50
tcp:
new: 60
established: 600
closed: 60
bypassed: 100
emergency-new: 5
emergency-established: 100
emergency-closed: 10
emergency-bypassed: 50
udp:
new: 30
established: 300
bypassed: 100
emergency-new: 10
emergency-established: 100
emergency-bypassed: 50
icmp:
new: 30
established: 300
bypassed: 100
emergency-new: 10
emergency-established: 100
emergency-bypassed: 50stream
Stream引擎用于跟踪TCP连接,它有两个模块,分别是TCP数据流的跟踪和数据包重组引擎,前者用于监视TCP连接的状态并确定一个完整的数据流,后者则用于将数据流进行重组以便让后续的处理模块能够识别。
首先是数据流跟踪模块的配置,和flow的一样,这里的memcap也是当前模块能占用内存的最大值;checksum_validation设置是否检查TCP数据包的CRC校验和,这个值用于保证数据包的完整性,如果设为yes则会丢弃那些校验失败的数据包;max_sessions对最大的TCP连接数进行了限制,防止其占用过多的内存;prealloc_sessions则是为了提高性能预先分配的连接数;midstream配置是否允许suricata从一个TCP连接的中间开始跟踪,出现这种情况几乎每次都会发生,因为当启动suricata时有部分TCP连接已经开始并处于建立连接的状态了,若设为true则表示可以从流中间跟踪,默认为false;async_oneside设置是否打开异步数据包处理,因为有时一个流可能不是从一个路由器而是多个不同的路由器进行传输,这样会导致数据包并不同步,true表示处理这种异步情况,默认为false。
Stream引擎的第二部分便是数据包重组,memcap就不做介绍了;因为数据包重组的代价比较大,需要的资源较多,为了避免无限制的重组超大数据包,depth对其进行了限制,默认为1MB;toserver_chunk_size和toclient_chunk_size只有超过设置的大小的原始数据包才会调用重组(字面上是这么理解):
# Stream engine settings. Here the TCP stream tracking and reassembly
# engine is configured.
#
# stream:
# memcap: 32mb # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a
# # number indicates it's in bytes.
# checksum-validation: yes # To validate the checksum of received
# # packet. If csum validation is specified as
# # "yes", then packet with invalid csum will not
# # be processed by the engine stream/app layer.
# # Warning: locally generated trafic can be
# # generated without checksum due to hardware offload
# # of checksum. You can control the handling of checksum
# # on a per-interface basis via the 'checksum-checks'
# # option
# prealloc-sessions: 2k # 2k sessions prealloc'd per stream thread
# midstream: false # don't allow midstream session pickups
# async-oneside: false # don't enable async stream handling
# inline: no # stream inline mode
# drop-invalid: yes # in inline mode, drop packets that are invalid with regards to streaming engine
# max-synack-queued: 5 # Max different SYN/ACKs to queue
# bypass: no # Bypass packets when stream.depth is reached
#
# reassembly:
# memcap: 64mb # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number
# # indicates it's in bytes.
# depth: 1mb # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number
# # indicates it's in bytes.
# toserver-chunk-size: 2560 # inspect raw stream in chunks of at least
# # this size. Can be specified in kb, mb,
# # gb. Just a number indicates it's in bytes.
# toclient-chunk-size: 2560 # inspect raw stream in chunks of at least
# # this size. Can be specified in kb, mb,
# # gb. Just a number indicates it's in bytes.
# randomize-chunk-size: yes # Take a random value for chunk size around the specified value.
# # This lower the risk of some evasion technics but could lead
# # detection change between runs. It is set to 'yes' by default.
# randomize-chunk-range: 10 # If randomize-chunk-size is active, the value of chunk-size is
# # a random value between (1 - randomize-chunk-range/100)*toserver-chunk-size
# # and (1 + randomize-chunk-range/100)*toserver-chunk-size and the same
# # calculation for toclient-chunk-size.
# # Default value of randomize-chunk-range is 10.
#
# raw: yes # 'Raw' reassembly enabled or disabled.
# # raw is for content inspection by detection
# # engine.
#
# segment-prealloc: 2048 # number of segments preallocated per thread
#
# check-overlap-different-data: true|false
# # check if a segment contains different data
# # than what we've already seen for that
# # position in the stream.
# # This is enabled automatically if inline mode
# # is used or when stream-event:reassembly_overlap_different_data;
# # is used in a rule.
#
stream:
memcap: 64mb
checksum-validation: yes # reject wrong csums
inline: auto # auto will use inline mode in IPS mode, yes or no set it statically
reassembly:
memcap: 256mb
depth: 1mb # reassemble 1mb into a stream
toserver-chunk-size: 2560
toclient-chunk-size: 2560
randomize-chunk-size: yes
#randomize-chunk-range: 10
#raw: yes
#segment-prealloc: 2048
#check-overlap-different-data: true而inline就看不大懂了,难道是选择yes就可以在IPS模式下工作,而no就不工作?官方文档中只提到了IDS和IPS模式下的流跟踪模块的不同,可以看到在IDS模式下只有服务端发送了ACK包suricata才会将之前监视的客户端数据包重组并进行下一步处理,而在IPS模式下由于需要实时监控并丢弃符合规则的包所以采用的是滑动窗口的方式,每当客户端发送一个数据包就会进行下一步处理:
IDS模式下
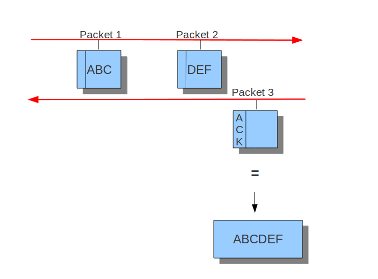
IPS模式下
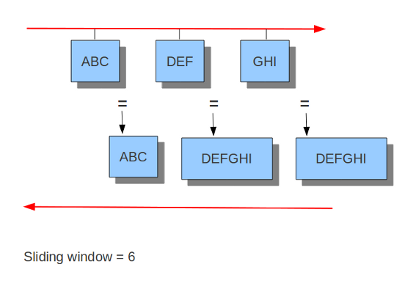
应用层解析器
如果希望Suricata解析应用层协议的数据包则需要对其进行配置。包括tls、ftp、smtp、ssh、http等。下面是部分默认的配置,enable可以选择yes、no或detection-only,yes表示既解析和检测数据包,detection-only则是只检测不做额外的解析,no则不检测也不解析:
# Configure the app-layer parsers. The protocols section details each
# protocol.
#
# The option "enabled" takes 3 values - "yes", "no", "detection-only".
# "yes" enables both detection and the parser, "no" disables both, and
# "detection-only" enables protocol detection only (parser disabled).
app-layer:
protocols:
tls:
enabled: yes
detection-ports:
dp: 443
# Completely stop processing TLS/SSL session after the handshake
# completed. If bypass is enabled this will also trigger flow
# bypass. If disabled (the default), TLS/SSL session is still
# tracked for Heartbleed and other anomalies.
#no-reassemble: yes
dcerpc:
enabled: yes
ftp:
enabled: yes
ssh:
enabled: yes
smtp:
enabled: yes
# Configure SMTP-MIME Decoder
mime:
# Decode MIME messages from SMTP transactions
# (may be resource intensive)
# This field supercedes all others because it turns the entire
# process on or off
decode-mime: yes
# Decode MIME entity bodies (ie. base64, quoted-printable, etc.)
decode-base64: yes
decode-quoted-printable: yes
# Maximum bytes per header data value stored in the data structure
# (default is 2000)
header-value-depth: 2000
# Extract URLs and save in state data structure
extract-urls: yes
# Set to yes to compute the md5 of the mail body. You will then
# be able to journalize it.
body-md5: no
# Configure inspected-tracker for file_data keyword
inspected-tracker:
content-limit: 100000
content-inspect-min-size: 32768
content-inspect-window: 4096
imap:
enabled: detection-only
msn:
enabled: detection-only
smb:
enabled: yes
detection-ports:
dp: 139, 445
# smb2 detection is disabled internally inside the engine.
#smb2:
# enabled: yes
# Note: NFS parser depends on Rust support: pass --enable-rust
# to configure.
nfs:
enabled: no
dns:
# memcaps. Globally and per flow/state.
#global-memcap: 16mb
#state-memcap: 512kb
# How many unreplied DNS requests are considered a flood.
# If the limit is reached, app-layer-event:dns.flooded; will match.
#request-flood: 500
tcp:
enabled: yes
detection-ports:
dp: 53
udp:
enabled: yes
detection-ports:
dp: 53
http:
enabled: yes
# memcap: 64mb
# default-config: Used when no server-config matches
# personality: List of personalities used by default
# request-body-limit: Limit reassembly of request body for inspection
# by http_client_body & pcre /P option.
# response-body-limit: Limit reassembly of response body for inspection
# by file_data, http_server_body & pcre /Q option.
# double-decode-path: Double decode path section of the URI
# double-decode-query: Double decode query section of the URI
# response-body-decompress-layer-limit:
# Limit to how many layers of compression will be
# decompressed. Defaults to 2.
#
# server-config: List of server configurations to use if address matches
# address: List of ip addresses or networks for this block
# personalitiy: List of personalities used by this block
# request-body-limit: Limit reassembly of request body for inspection
# by http_client_body & pcre /P option.
# response-body-limit: Limit reassembly of response body for inspection
# by file_data, http_server_body & pcre /Q option.
# double-decode-path: Double decode path section of the URI
# double-decode-query: Double decode query section of the URI
#
# uri-include-all: Include all parts of the URI. By default the
# 'scheme', username/password, hostname and port
# are excluded. Setting this option to true adds
# all of them to the normalized uri as inspected
# by http_uri, urilen, pcre with /U and the other
# keywords that inspect the normalized uri.
# Note that this does not affect http_raw_uri.
# Also, note that including all was the default in
# 1.4 and 2.0beta1.
#
# meta-field-limit: Hard size limit for request and response size
# limits. Applies to request line and headers,
# response line and headers. Does not apply to
# request or response bodies. Default is 18k.
# If this limit is reached an event is raised.
#
# Currently Available Personalities:
# Minimal, Generic, IDS (default), IIS_4_0, IIS_5_0, IIS_5_1, IIS_6_0,
# IIS_7_0, IIS_7_5, Apache_2
libhtp:
default-config:
personality: IDS
# Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates
# it's in bytes.
request-body-limit: 100kb
response-body-limit: 100kb
# inspection limits
request-body-minimal-inspect-size: 32kb
request-body-inspect-window: 4kb
response-body-minimal-inspect-size: 40kb
response-body-inspect-window: 16kb
# response body decompression (0 disables)
response-body-decompress-layer-limit: 2
# auto will use http-body-inline mode in IPS mode, yes or no set it statically
http-body-inline: auto
# Take a random value for inspection sizes around the specified value.
# This lower the risk of some evasion technics but could lead
# detection change between runs. It is set to 'yes' by default.
#randomize-inspection-sizes: yes
# If randomize-inspection-sizes is active, the value of various
# inspection size will be choosen in the [1 - range%, 1 + range%]
# range
# Default value of randomize-inspection-range is 10.
#randomize-inspection-range: 10
# decoding
double-decode-path: no
double-decode-query: no
server-config:
#- apache:
# address: [192.168.1.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8, "::1"]
# personality: Apache_2
# # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates
# # it's in bytes.
# request-body-limit: 4096
# response-body-limit: 4096
# double-decode-path: no
# double-decode-query: no
#- iis7:
# address:
# - 192.168.0.0/24
# - 192.168.10.0/24
# personality: IIS_7_0
# # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates
# # it's in bytes.
# request-body-limit: 4096
# response-body-limit: 4096
# double-decode-path: no
# double-decode-query: no
# Note: Modbus probe parser is minimalist due to the poor significant field
# Only Modbus message length (greater than Modbus header length)
# And Protocol ID (equal to 0) are checked in probing parser
# It is important to enable detection port and define Modbus port
# to avoid false positive
modbus:
# How many unreplied Modbus requests are considered a flood.
# If the limit is reached, app-layer-event:modbus.flooded; will match.
#request-flood: 500
enabled: no
detection-ports:
dp: 502
# According to MODBUS Messaging on TCP/IP Implementation Guide V1.0b, it
# is recommended to keep the TCP connection opened with a remote device
# and not to open and close it for each MODBUS/TCP transaction. In that
# case, it is important to set the depth of the stream reassembling as
# unlimited (stream.reassembly.depth: 0)
# Stream reassembly size for modbus. By default track it completely.
stream-depth: 0
# DNP3
dnp3:
enabled: no
detection-ports:
dp: 20000
# SCADA EtherNet/IP and CIP protocol support
enip:
enabled: no
detection-ports:
dp: 44818
sp: 44818
# Note: parser depends on experimental Rust support
# with --enable-rust-experimental passed to configure
ntp:
enabled: no
由于http协议的数据包比较复杂和常用,且它的解析器使用第三方库,因此下面对其单独说明。
libhtp
Suricata使用libhtp库对HTTP会话数据包进行解析。由于http的web服务器种类非常多导致了suricata必须处理每一种不同服务器所产生的http流量,用户在这里可以配置IP地址和web服务器种类的对应关系。可以选择的web服务器包括,默认的是IDS模式的服务器:
Minimal
Generic
IDS (default)
IIS_4_0
IIS_5_0
IIS_5_1
IIS_6_0
IIS_7_0
IIS_7_5
Apache_2在每一种模式下可以配置IP地址、web服务器种类以及对request、response数据包大小的限制,默认的IDS模式表示所有的IP都使用这套配置。一套典型的配置如下,前面几项配置都容易理解double-decode-path和double-decode-query需要进行特殊说明。有些攻击web服务器的手法是通过在URI中加入特定的攻击字段来完成,URI由协议、主机名、端口号(大部分http协议是80端口,因此可省略)、路径和查询参数五部分组成(详情参考统一资源定位符-维基百科),能够控制的便是路径和查询参数,double-decode-path和double-decode-query就是可以检查这两部分是否经过了双重URL编码(可参考Double Encoding-OWASP):
http:
enabled: yes
# memcap: 64mb
# default-config: Used when no server-config matches
# personality: List of personalities used by default
# request-body-limit: Limit reassembly of request body for inspection
# by http_client_body & pcre /P option.
# response-body-limit: Limit reassembly of response body for inspection
# by file_data, http_server_body & pcre /Q option.
# double-decode-path: Double decode path section of the URI
# double-decode-query: Double decode query section of the URI
# response-body-decompress-layer-limit:
# Limit to how many layers of compression will be
# decompressed. Defaults to 2.
#
# server-config: List of server configurations to use if address matches
# address: List of ip addresses or networks for this block
# personalitiy: List of personalities used by this block
# request-body-limit: Limit reassembly of request body for inspection
# by http_client_body & pcre /P option.
# response-body-limit: Limit reassembly of response body for inspection
# by file_data, http_server_body & pcre /Q option.
# double-decode-path: Double decode path section of the URI
# double-decode-query: Double decode query section of the URI
#
# uri-include-all: Include all parts of the URI. By default the
# 'scheme', username/password, hostname and port
# are excluded. Setting this option to true adds
# all of them to the normalized uri as inspected
# by http_uri, urilen, pcre with /U and the other
# keywords that inspect the normalized uri.
# Note that this does not affect http_raw_uri.
# Also, note that including all was the default in
# 1.4 and 2.0beta1.
#
# meta-field-limit: Hard size limit for request and response size
# limits. Applies to request line and headers,
# response line and headers. Does not apply to
# request or response bodies. Default is 18k.
# If this limit is reached an event is raised.
#
# Currently Available Personalities:
# Minimal, Generic, IDS (default), IIS_4_0, IIS_5_0, IIS_5_1, IIS_6_0,
# IIS_7_0, IIS_7_5, Apache_2
libhtp:
default-config:
personality: IDS
# Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates
# it's in bytes.
request-body-limit: 100kb
response-body-limit: 100kb
# inspection limits
request-body-minimal-inspect-size: 32kb
request-body-inspect-window: 4kb
response-body-minimal-inspect-size: 40kb
response-body-inspect-window: 16kb
# response body decompression (0 disables)
response-body-decompress-layer-limit: 2
# auto will use http-body-inline mode in IPS mode, yes or no set it statically
http-body-inline: auto
# Take a random value for inspection sizes around the specified value.
# This lower the risk of some evasion technics but could lead
# detection change between runs. It is set to 'yes' by default.
#randomize-inspection-sizes: yes
# If randomize-inspection-sizes is active, the value of various
# inspection size will be choosen in the [1 - range%, 1 + range%]
# range
# Default value of randomize-inspection-range is 10.
#randomize-inspection-range: 10
# decoding
double-decode-path: no
double-decode-query: no
server-config:
#- apache:
# address: [192.168.1.0/24, 127.0.0.0/8, "::1"]
# personality: Apache_2
# # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates
# # it's in bytes.
# request-body-limit: 4096
# response-body-limit: 4096
# double-decode-path: no
# double-decode-query: no
#- iis7:
# address:
# - 192.168.0.0/24
# - 192.168.10.0/24
# personality: IIS_7_0
# # Can be specified in kb, mb, gb. Just a number indicates
# # it's in bytes.
# request-body-limit: 4096
# response-body-limit: 4096
# double-decode-path: no
# double-decode-query: noasn1-max-frames
Asn1是一种标准的描述数据和结构体的标准符号,大量用于通信和计算机网络中解码和传输数据,详细可以参考Abstract Syntax Notation One-维基百科。这里就是配置使用asn1进行解码的数据包的最大数量:
# Limit for the maximum number of asn1 frames to decode (default 256)
asn1-max-frames: 256

