
FastAPI教程 元数据和文档 URL
你可以在 FastAPI 应用中自定义几个元数据配置。
标题、描述和版本
你可以设定:
- Title:在 OpenAPI 和自动 API 文档用户界面中作为 API 的标题/名称使用。
- Description:在 OpenAPI 和自动 API 文档用户界面中用作 API 的描述。
- Version:API 版本,例如 v2 或者 2.5.0。如果你之前的应用程序版本也使用 OpenAPI 会很有用。
使用 title、description 和 version 来设置它们:
from fastapi import FastAPI
description = """
ChimichangApp API helps you do awesome stuff. ????
## Items
You can **read items**.
## Users
You will be able to:
* **Create users** (_not implemented_).
* **Read users** (_not implemented_).
"""
app = FastAPI(
title="ChimichangApp",
description=description,
version="0.0.1",
terms_of_service="http://example.com/terms/",
contact={
"name": "Deadpoolio the Amazing",
"url": "http://x-force.example.com/contact/",
"email": "dp@x-force.example.com",
},
license_info={
"name": "Apache 2.0",
"url": "https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html",
},
)
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Katana"}]
通过这样设置,自动 API 文档看起来会像:
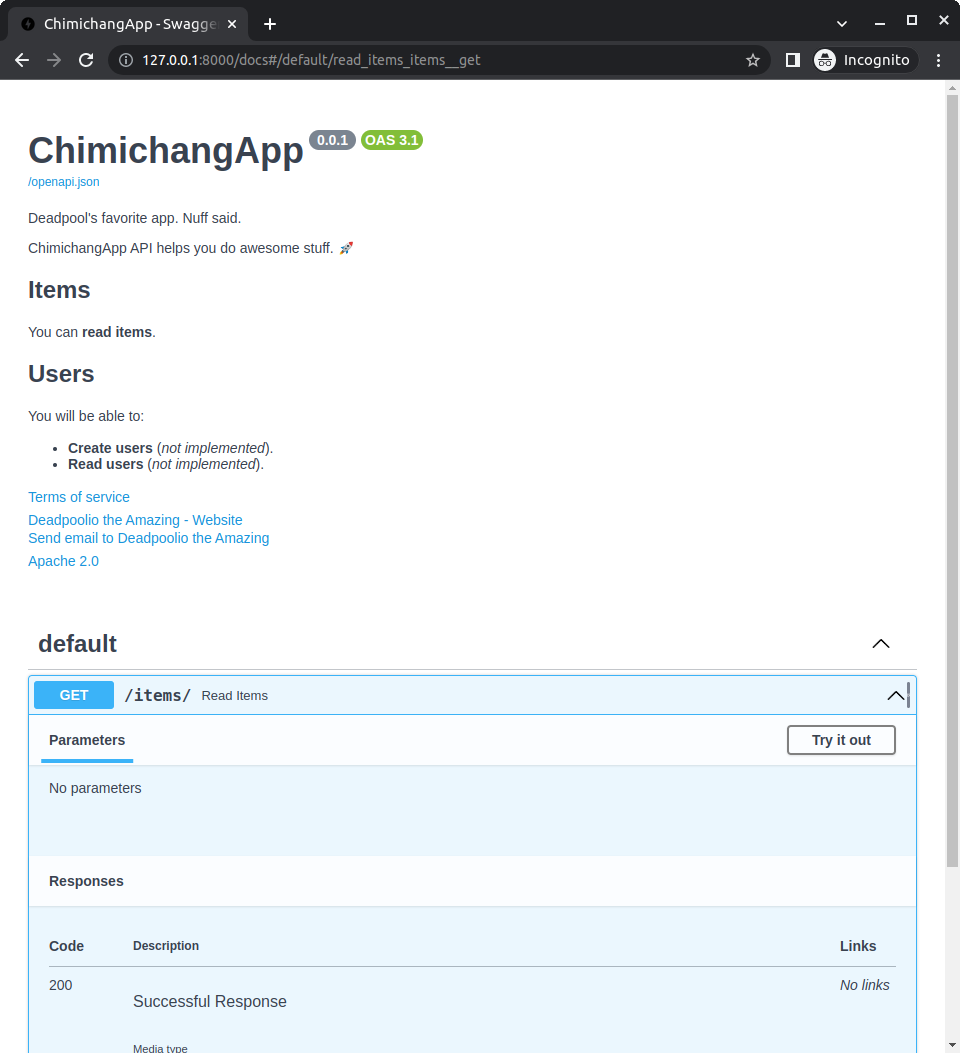
标签元数据
你也可以使用参数 openapi_tags,为用于分组路径操作的不同标签添加额外的元数据。
它接受一个列表,这个列表包含每个标签对应的一个字典。
每个字典可以包含:
- name(必要):一个 str,它与路径操作和 APIRouter 中使用的 tags 参数有相同的标签名。
- description:一个用于简短描述标签的 str。它支持 Markdown 并且会在文档用户界面中显示。
- externalDocs:一个描述外部文档的 dict:description:用于简短描述外部文档的 str。url(必要):外部文档的 URL str。
创建标签元数据
让我们在带有标签的示例中为 users 和 items 试一下。
创建标签元数据并把它传递给 openapi_tags 参数:
from fastapi import FastAPI
tags_metadata = [
{
"name": "users",
"description": "Operations with users. The **login** logic is also here.",
},
{
"name": "items",
"description": "Manage items. So _fancy_ they have their own docs.",
"externalDocs": {
"description": "Items external docs",
"url": "https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/",
},
},
]
app = FastAPI(openapi_tags=tags_metadata)
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def get_users():
return [{"name": "Harry"}, {"name": "Ron"}]
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def get_items():
return [{"name": "wand"}, {"name": "flying broom"}]
注意你可以在描述内使用 Markdown,例如「login」会显示为粗体(login)以及「fancy」会显示为斜体(fancy)。
提示
不必为你使用的所有标签都添加元数据。
使用你的标签
将 tags 参数和路径操作(以及 APIRouter)一起使用,将其分配给不同的标签:
from fastapi import FastAPI
tags_metadata = [
{
"name": "users",
"description": "Operations with users. The **login** logic is also here.",
},
{
"name": "items",
"description": "Manage items. So _fancy_ they have their own docs.",
"externalDocs": {
"description": "Items external docs",
"url": "https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/",
},
},
]
app = FastAPI(openapi_tags=tags_metadata)
@app.get("/users/", tags=["users"])
async def get_users():
return [{"name": "Harry"}, {"name": "Ron"}]
@app.get("/items/", tags=["items"])
async def get_items():
return [{"name": "wand"}, {"name": "flying broom"}]
信息
阅读更多关于标签的信息路径操作配置。
查看文档
如果你现在查看文档,它们会显示所有附加的元数据:
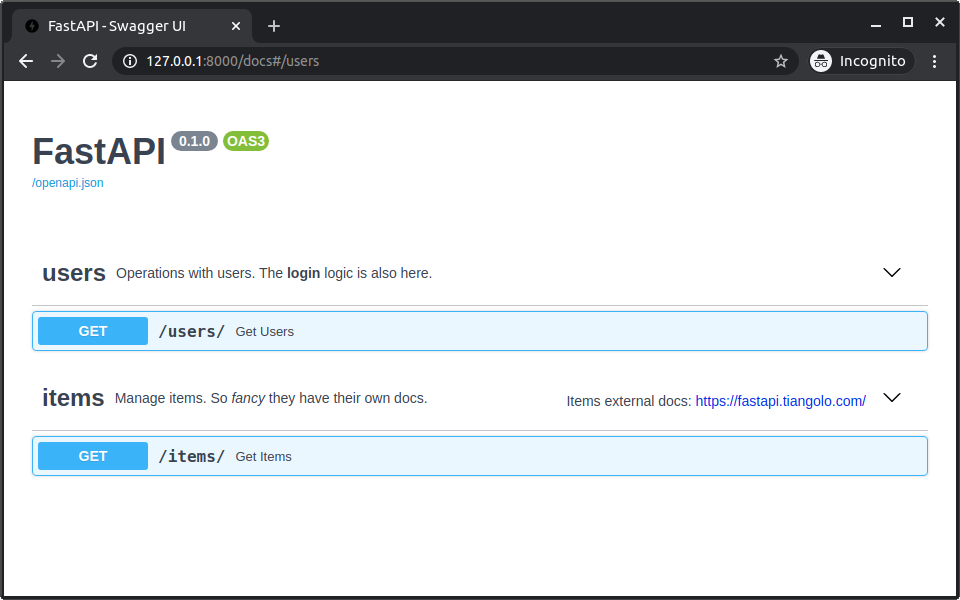
标签顺序
每个标签元数据字典的顺序也定义了在文档用户界面显示的顺序。
例如按照字母顺序,即使 users 排在 items 之后,它也会显示在前面,因为我们将它的元数据添加为列表内的第一个字典。
OpenAPI URL
默认情况下,OpenAPI 模式服务于 /openapi.json。
但是你可以通过参数 openapi_url 对其进行配置。
例如,将其设置为服务于 /api/v1/openapi.json:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI(openapi_url="/api/v1/openapi.json")
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo"}]
如果你想完全禁用 OpenAPI 模式,可以将其设置为 openapi_url=None,这样也会禁用使用它的文档用户界面。
文档 URLs
你可以配置两个文档用户界面,包括:
- Swagger UI:服务于 /docs。可以使用参数 docs_url 设置它的 URL。可以通过设置 docs_url=None 禁用它。
- ReDoc:服务于 /redoc。可以使用参数 redoc_url 设置它的 URL。可以通过设置 redoc_url=None 禁用它。
例如,设置 Swagger UI 服务于 /documentation 并禁用 ReDoc:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI(docs_url="/documentation", redoc_url=None)
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"name": "Foo"}]