
UIAbility组件与UI的数据同步
基于HarmonyOS的应用模型,可以通过以下两种方式来实现UIAbility组件与UI之间的数据同步。
- 使用EventHub进行数据通信:基于发布订阅模式来实现,事件需要先订阅后发布,订阅者收到消息后进行处理。
- 使用globalThis进行数据同步:ArkTS引擎实例内部的一个全局对象,在ArkTS引擎实例内部都能访问。
- 使用AppStorage/LocalStorage进行数据同步:ArkUI提供了AppStorage和LocalStorage两种应用级别的状态管理方案,可用于实现应用级别和UIAbility级别的数据同步。
使用EventHub进行数据通信
EventHub提供了UIAbility组件/ExtensionAbility组件级别的事件机制,以UIAbility组件/ExtensionAbility组件为中心提供了订阅、取消订阅和触发事件的数据通信能力。接口说明请参见EventHub。
在使用EventHub之前,首先需要获取EventHub对象。基类Context提供了EventHub对象,本章节以使用EventHub实现UIAbility与UI之间的数据通信为例进行说明。
在UIAbility中调用eventHub.on()方法注册一个自定义事件“event1”,eventHub.on()有如下两种调用方式,使用其中一种即可。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility';
- const TAG: string = '[Example].[Entry].[EntryAbility]';
- export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
- func1(...data) {
- // 触发事件,完成相应的业务操作
- console.info(TAG, '1. ' + JSON.stringify(data));
- }
- onCreate(want, launch) {
- // 获取eventHub
- let eventhub = this.context.eventHub;
- // 执行订阅操作
- eventhub.on('event1', this.func1);
- eventhub.on('event1', (...data) => {
- // 触发事件,完成相应的业务操作
- console.info(TAG, '2. ' + JSON.stringify(data));
- });
- }
- }
在UI界面中通过eventHub.emit()方法触发该事件,在触发事件的同时,根据需要传入参数信息。
- import common from '@ohos.app.ability.common';
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct Index {
- private context = getContext(this) as common.UIAbilityContext;
- eventHubFunc() {
- // 不带参数触发自定义“event1”事件
- this.context.eventHub.emit('event1');
- // 带1个参数触发自定义“event1”事件
- this.context.eventHub.emit('event1', 1);
- // 带2个参数触发自定义“event1”事件
- this.context.eventHub.emit('event1', 2, 'test');
- // 开发者可以根据实际的业务场景设计事件传递的参数
- }
- // 页面展示
- build() {
- // ...
- }
- }
在UIAbility的注册事件回调中可以得到对应的触发事件结果,运行日志结果如下所示。
- []
- [1]
- [2,'test']
在自定义事件“event1”使用完成后,可以根据需要调用eventHub.off()方法取消该事件的订阅。
- // context为UIAbility实例的AbilityContext
- this.context.eventHub.off('event1');
使用globalThis进行数据同步
globalThis是ArkTS引擎实例内部的一个全局对象,引擎内部的UIAbility/ExtensionAbility/Page都可以使用,因此可以使用globalThis全局对象进行数据同步。
图1 使用globalThis进行数据同步
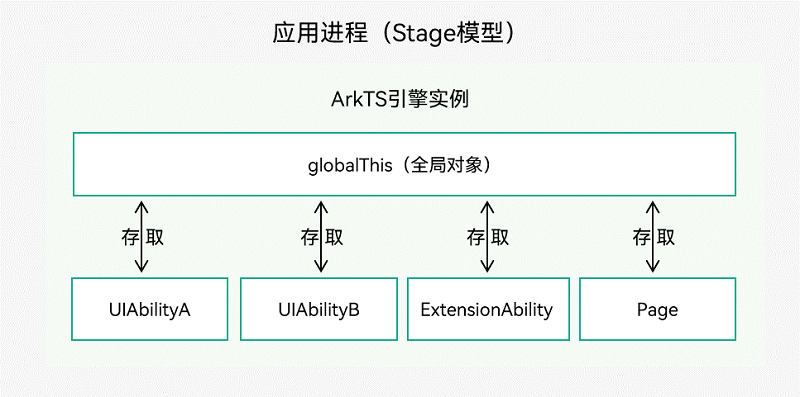
如上图所示,下面来具体介绍globalThis的使用:
UIAbility和Page之间使用globalThis
globalThis为ArkTS引擎实例下的全局对象,可以通过globalThis绑定属性/方法来进行UIAbility组件与UI的数据同步。例如在UIAbility组件中绑定want参数,即可在UIAbility对应的UI界面上使用want参数信息。
调用startAbility()方法启动一个UIAbility实例时,被启动的UIAbility创建完成后会进入onCreate()生命周期回调,且在onCreate()生命周期回调中能够接受到传递过来的want参数,可以将want参数绑定到globalThis上。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'
- export default class EntryAbility extends UIAbility {
- onCreate(want, launch) {
- globalThis.entryAbilityWant = want;
- // ...
- }
- // ...
- }
在UI界面中即可通过globalThis获取到want参数信息。
- let entryAbilityWant;
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct Index {
- aboutToAppear() {
- entryAbilityWant = globalThis.entryAbilityWant;
- }
- // 页面展示
- build() {
- // ...
- }
- }
UIAbility和UIAbility之间使用globalThis
同一个应用中UIAbility和UIAbility之间的数据传递,可以通过将数据绑定到全局变量globalThis上进行同步,如在AbilityA中将数据保存在globalThis,然后跳转到AbilityB中取得该数据:
AbilityA中保存数据一个字符串数据并挂载到globalThis上。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'
- export default class AbilityA extends UIAbility {
- onCreate(want, launch) {
- globalThis.entryAbilityStr = 'AbilityA'; // AbilityA存放字符串“AbilityA”到globalThis
- // ...
- }
- }
AbilityB中获取对应的数据。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'
- export default class AbilityB extends UIAbility {
- onCreate(want, launch) {
- // AbilityB从globalThis读取name并输出
- console.info('name from entryAbilityStr: ' + globalThis.entryAbilityStr);
- // ...
- }
- }
globalThis使用的注意事项
图2 globalThis注意事项
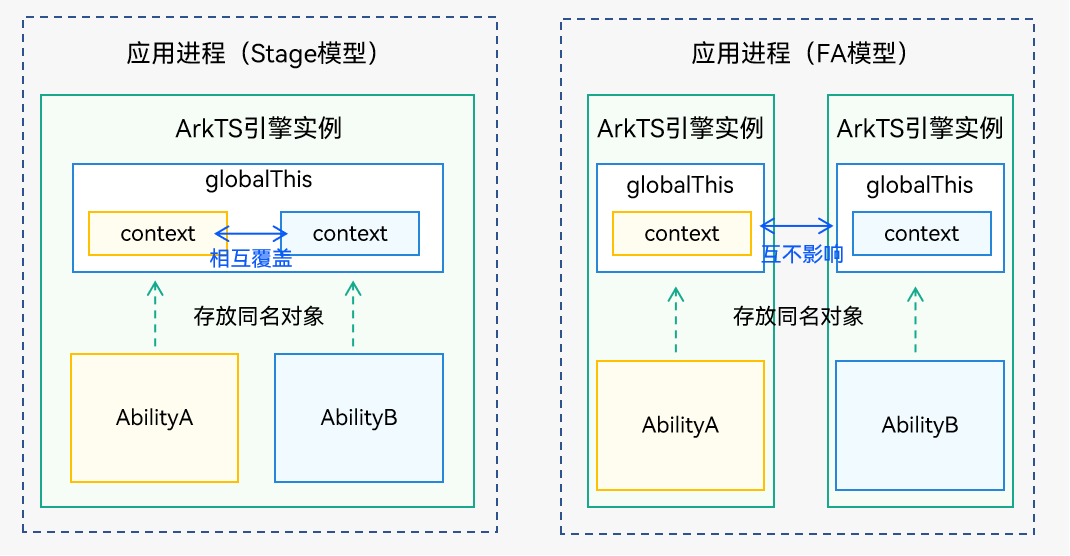
Stage模型下进程内的UIAbility组件共享ArkTS引擎实例,使用globalThis时需要避免存放相同名称的对象。例如AbilityA和AbilityB可以使用globalThis共享数据,在存放相同名称的对象时,先存放的对象会被后存放的对象覆盖。
FA模型因为每个UIAbility组件之间引擎隔离,不会存在该问题。
对于绑定在globalThis上的对象,其生命周期与ArkTS虚拟机实例相同,建议在使用完成之后将其赋值为null,以减少对应用内存的占用。
Stage模型上同名对象覆盖导致问题的场景举例说明。
在AbilityA文件中使用globalThis存放了UIAbilityContext。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'
- export default class AbilityA extends UIAbility {
- onCreate(want, launch) {
- globalThis.context = this.context; // AbilityA存放context到globalThis
- // ...
- }
- }
在AbilityA的页面中获取该UIAbilityContext并进行使用。使用完成后将AbilityA实例切换至后台。
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct Index {
- onPageShow() {
- let ctx = globalThis.context; // 页面中从globalThis中取出context并使用
- let permissions = ['com.example.permission']
- ctx.requestPermissionsFromUser(permissions,(result) => {
- // ...
- });
- }
- // 页面展示
- build() {
- // ...
- }
- }
在AbilityB文件中使用globalThis存放了UIAbilityContext,并且命名为相同的名称。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'
- export default class AbilityB extends UIAbility {
- onCreate(want, launch) {
- // AbilityB覆盖了AbilityA在globalThis中存放的context
- globalThis.context = this.context;
- // ...
- }
- }
在AbilityB的页面中获取该UIAbilityContext并进行使用。此时获取到的globalThis.context已经表示为AbilityB中赋值的UIAbilityContext内容。
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct Index {
- onPageShow() {
- let ctx = globalThis.context; // Page中从globalThis中取出context并使用
- let permissions = ['com.example.permission']
- ctx.requestPermissionsFromUser(permissions,(result) => {
- console.info('requestPermissionsFromUser result:' + JSON.stringify(result));
- });
- }
- // 页面展示
- build() {
- // ...
- }
- }
在AbilityB实例切换至后台,将AbilityA实例从后台切换回到前台。此时AbilityA的onCreate生命周期不会再次进入。
- import UIAbility from '@ohos.app.ability.UIAbility'
- export default class AbilityA extends UIAbility {
- onCreate(want, launch) { // AbilityA从后台进入前台,不会再走这个生命周期
- globalThis.context = this.context;
- // ...
- }
- }
在AbilityA的页面再次回到前台时,其获取到的globalThis.context表示的为AbilityB的UIAbilityContext,而不是AbilityA的UIAbilityContext,在AbilityA的页面中使用则会出错。
- @Entry
- @Component
- struct Index {
- onPageShow() {
- let ctx = globalThis.context; // 这时候globalThis中的context是AbilityB的context
- let permissions=['com.example.permission'];
- ctx.requestPermissionsFromUser(permissions,(result) => { // 使用这个对象就会导致进程崩溃
- console.info('requestPermissionsFromUser result:' + JSON.stringify(result));
- });
- }
- // 页面展示
- build() {
- // ...
- }
- }
使用AppStorage/LocalStorage进行数据同步
ArkUI提供了AppStorage和LocalStorage两种应用级别的状态管理方案,可用于实现应用级别和UIAbility级别的数据同步。使用这些方案可以方便地管理应用状态,提高应用性能和用户体验。其中,AppStorage是一个全局的状态管理器,适用于多个UIAbility共享同一状态数据的情况;而LocalStorage则是一个局部的状态管理器,适用于单个UIAbility内部使用的状态数据。通过这两种方案,开发者可以更加灵活地控制应用状态,提高应用的可维护性和可扩展性。详细请参见应用级变量的状态管理。